Language Localization for Canadian Audiences
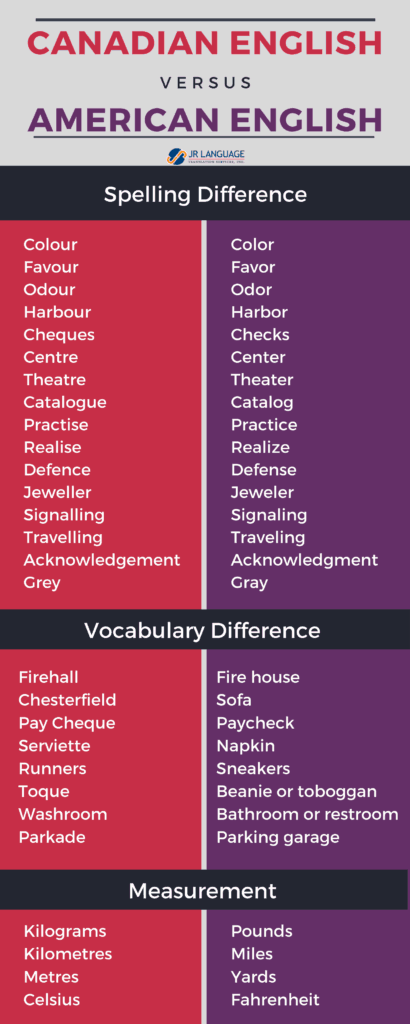
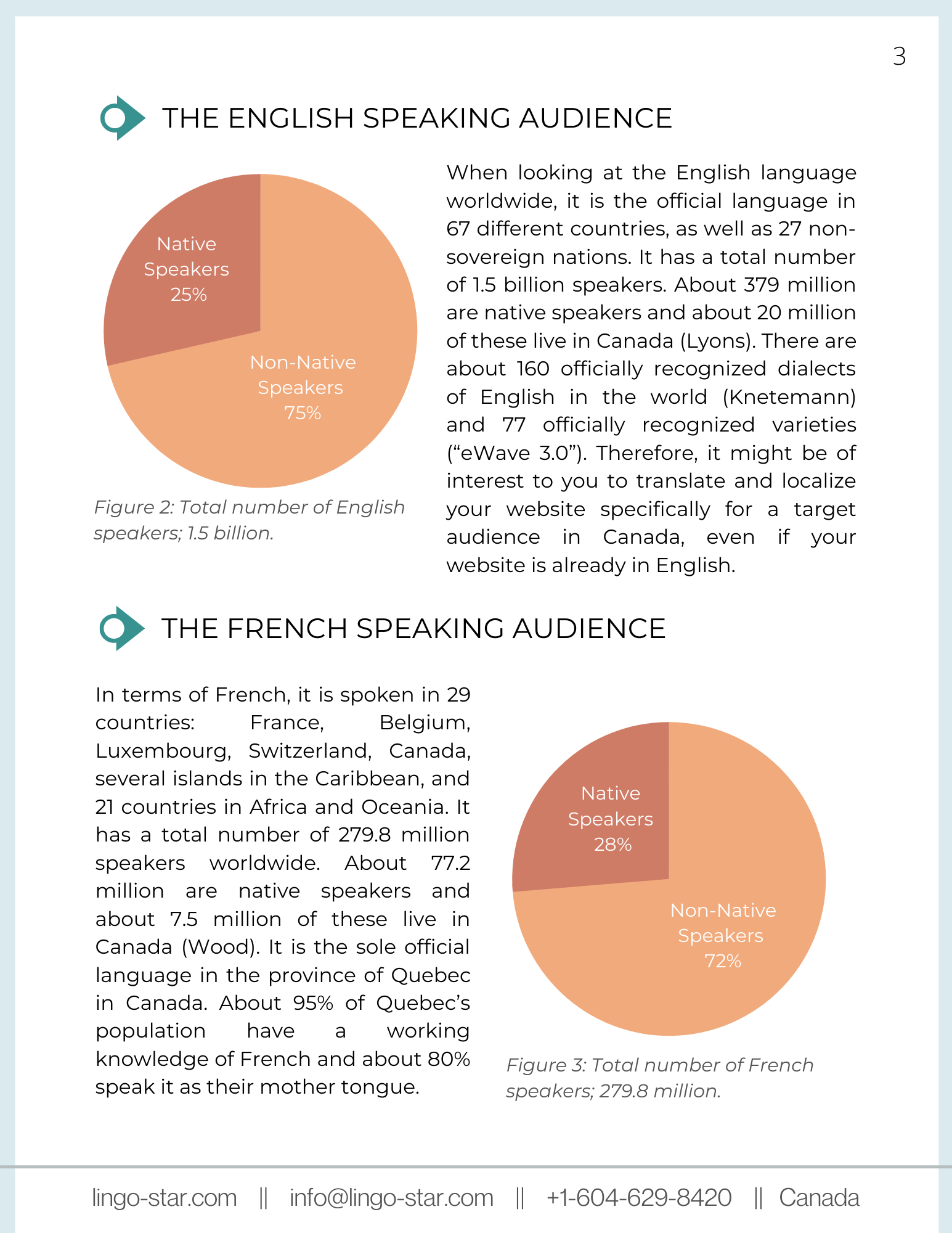
Language localization for Canadian audiences involves adapting content to meet the linguistic, cultural, and regulatory requirements of Canada’s diverse population. Canada is officially bilingual, with English and French as the two main languages, but localization goes beyond simple translation to ensure cultural relevance and compliance with local laws.
Key Considerations
1. Bilingualism and Regional Variations
- Canada recognizes both English and French as official languages.
- Quebec is predominantly Francophone and has strict language laws (e.g., Bill 101, Bill 96) requiring French in public life, business, and digital content.
- New Brunswick is officially bilingual, requiring services and communications in both languages.
- Other provinces are mainly English-speaking, but federal services must be bilingual, and regions with significant Francophone populations may have additional French language requirements.
2. Cultural Sensitivity
- Localization must account for cultural nuances, regional preferences, and historical sensitivities.
- In Quebec, avoid politically sensitive terms (e.g., "Canada" or "Canadian") and use terms like "national" or "country" instead.
- Use native translators who understand local idioms, expressions, and cultural references.
3. Legal and Regulatory Compliance
- Quebec’s language laws require French in product packaging, instructions, signage, and commercial advertising.
- Digital content, social media, and e-commerce platforms must also comply with these regulations.
4. Best Practices
- Use Native Translators: Native speakers ensure natural, culturally appropriate language.
- Prioritize Cultural Adaptation: Avoid literal translations; adapt content to resonate with local audiences.
- Identify All Customer Touchpoints: Ensure every interaction (website, app, customer service) is localized.
- Build a Strong Localization Team: Include managers, linguists, designers, and marketers.
- Choose the Right Tools: Use translation management systems (TMS), machine translation, and quality assurance tools to streamline the process.
5. Linguistic Duality
- Promote both English and French in Canadian society, as mandated by the Official Languages Act.
- Foster appreciation and cooperation between English and French speakers.
Steps in the Localization Process
- Develop a Localization Strategy: Define goals and establish a workflow tailored to the Canadian market.
- Build a Localization Team: Assemble experts in translation, design, and marketing.
- Choose Localization Tools: Use TMS, machine translation, and QA tools to enhance efficiency.
- Translate and Adapt Content: Ensure linguistic and cultural accuracy.
- Review and Test: Conduct quality assurance and user testing to ensure the localized content meets local expectations.
Conclusion
Effective language localization for Canadian audiences requires a deep understanding of regional language use, cultural nuances, and legal requirements. By following best practices and leveraging the right tools and teams, businesses can successfully engage with Canada’s diverse population and build lasting brand loyalty.



)














Maple Ranking offers the highest quality website traffic services in Canada. We provide a variety of traffic services for our clients, including website traffic, desktop traffic, mobile traffic, Google traffic, search traffic, eCommerce traffic, YouTube traffic, and TikTok traffic. Our website boasts a 100% customer satisfaction rate, so you can confidently purchase large amounts of SEO traffic online. For just 720 PHP per month, you can immediately increase website traffic, improve SEO performance, and boost sales!
Having trouble choosing a traffic package? Contact us, and our staff will assist you.
Free consultation