Overview of Multilingual and Multimodal Conversations
Multilingual and multimodal conversations refer to interactions that involve multiple languages and combine various communication modes—such as text, speech, images, and gestures—to convey meaning. These types of conversations are increasingly important in both human-to-human and human-to-machine communication, especially in diverse, globalized, and technologically integrated environments.
Key Concepts
Multilingualism in conversation means that participants may use, understand, or switch between two or more languages during the interaction. This is common in multicultural societies and is supported by technologies like machine translation and multilingual large language models (LLMs).
Multimodality refers to the use of multiple sensory channels or modes (e.g., visual, auditory, tactile) to communicate. In practice, this could mean a conversation that includes spoken words, written text, images, gestures, or even physical interactions.
Technological Advances
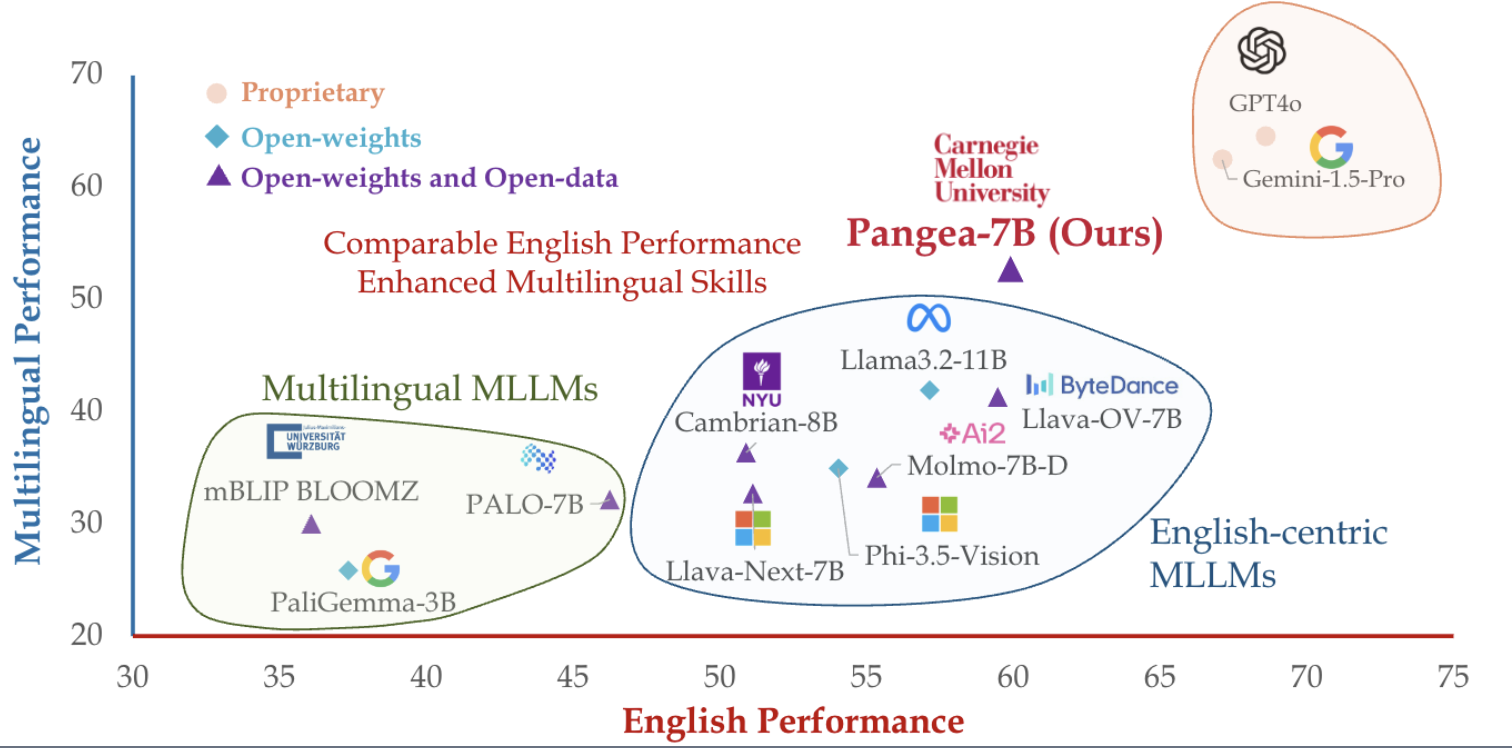
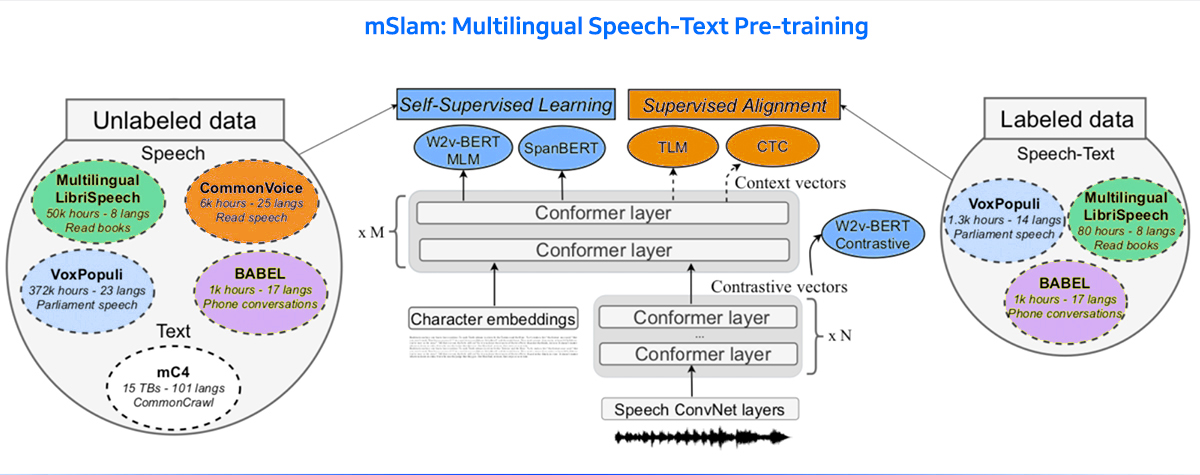
Recent research has focused on building multilingual multimodal dialogue systems that can understand and generate responses across languages and modalities. For example, systems like Pangea are trained on datasets spanning dozens of languages and can handle tasks such as image captioning, visual question answering, and natural conversation in multiple languages. These systems aim to be inclusive, supporting not just widely spoken languages but also under-resourced ones, by leveraging transfer learning and large-scale multilingual datasets.
Challenges include accurately recognizing speakers and addressees in multi-party settings, understanding the structure of conversations (who is speaking to whom, and about what), and seamlessly integrating visual and linguistic information—especially when words are ambiguous without visual context. Current models perform better when audio and visual cues are clear, but struggle with anonymized or noisy data.
Applications and User Experience
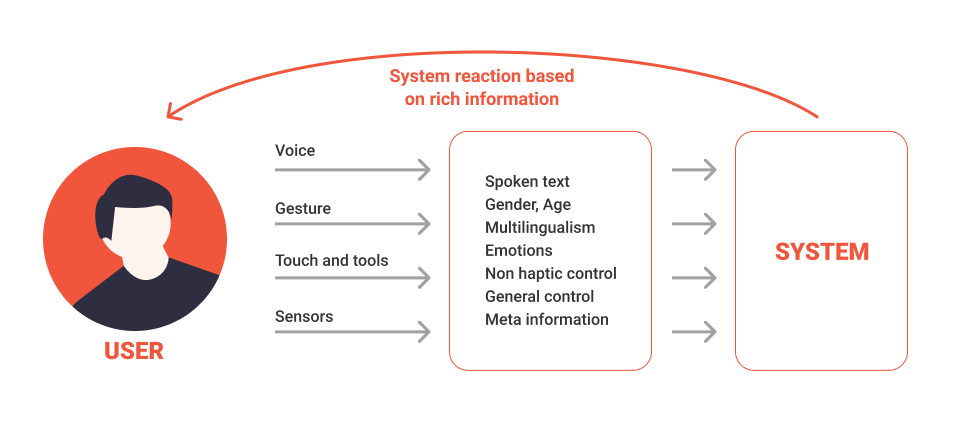
Multimodal design improves user experience by allowing people to interact in the most natural or convenient way for their context. For instance, a smart home assistant might accept voice commands, display visual information, and allow touch input—all within the same conversation flow. This flexibility is especially valuable for multilingual users, who may prefer different modes depending on the situation or their language proficiency.
In education, multimodal strategies—such as using visuals, gestures, and multiple languages—help create inclusive environments where learners can demonstrate understanding in varied ways, supporting both content mastery and language development.
Research Directions
- Cross-modal representation learning: Developing models that can connect visual information with text in multiple languages, improving tasks like machine translation of ambiguous terms.
- Conversation structure understanding: Building systems that can track who is speaking, to whom, and about what, especially in face-to-face, multi-party settings.
- Inclusivity and accessibility: Ensuring that technologies support a wide range of languages and cultural contexts, not just those dominant in existing datasets.
Summary Table: Multilingual vs. Multimodal Aspects
| Aspect | Multilingual Conversations | Multimodal Conversations |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Language diversity and switching | Use of multiple communication modes |
| Key Technologies | Machine translation, multilingual LLMs | Vision-language models, speech recognition |
| Challenges | Ambiguity, low-resource languages | Integrating modalities, context awareness |
| Applications | Global communication, education | Smart assistants, accessible interfaces |
Future Outlook
The field is moving toward more robust, inclusive, and context-aware systems that can handle the complexity of real-world multilingual, multimodal interactions. Open datasets, transparent models, and evaluation benchmarks are critical for progress, as is attention to the needs of speakers of less-resourced languages. Advances here will enable more natural, effective, and equitable communication across linguistic and cultural boundaries.

















Maple Ranking offers the highest quality website traffic services in Canada. We provide a variety of traffic services for our clients, including website traffic, desktop traffic, mobile traffic, Google traffic, search traffic, eCommerce traffic, YouTube traffic, and TikTok traffic. Our website boasts a 100% customer satisfaction rate, so you can confidently purchase large amounts of SEO traffic online. For just 720 PHP per month, you can immediately increase website traffic, improve SEO performance, and boost sales!
Having trouble choosing a traffic package? Contact us, and our staff will assist you.
Free consultation