Hardware RAID vs Software RAID: Pros, Cons, and Performance Implications
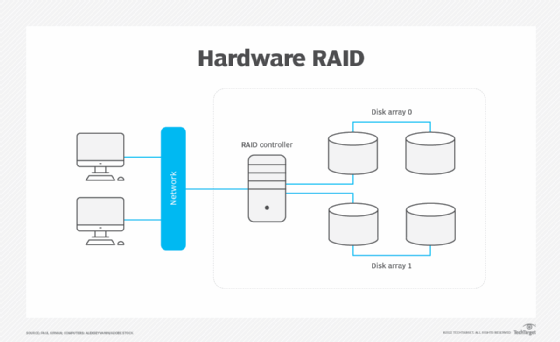
Hardware RAID uses a dedicated RAID controller with its own processor and memory to manage the RAID array independently of the host system's CPU. Software RAID relies on the host system’s CPU and operating system to manage the RAID functions via software drivers.
| Aspect | Hardware RAID | Software RAID |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | More expensive due to dedicated RAID controller hardware | More economical; no extra hardware needed |
| Performance | Offloads RAID processing from CPU, often better for heavy I/O workloads; supports write-back cache with battery backup for enhanced write performance | Uses host CPU for RAID tasks, which can impact system performance under heavy load, but modern CPUs often mitigate this impact |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; tied to specific RAID controller hardware; replacing controller requires compatible hardware | More flexible; supports multiple RAID levels and easier to reconfigure; tied to OS but portable across systems with same OS |
| Compatibility | Independent of OS; can be used across multiple operating systems | Dependent on OS and driver compatibility; may face challenges when migrating or upgrading OS |
| Ease of Setup and Management | Usually simpler for end users once hardware is installed; less user interaction needed for RAID management | Requires more user interaction and OS-level management; setup integrated with OS utilities |
| Scalability | Limited by controller capabilities and number of supported drives | Typically supports more drives and easier to expand or reconfigure |
| Data Recovery and Reliability | Often includes advanced features like battery-backed cache and dedicated monitoring, improving data protection and recovery | Lacks hardware-level protections like battery-backed cache; recovery depends on OS tools and software robustness |
Performance Implications:
-
Hardware RAID generally provides better performance for intensive RAID levels (e.g., RAID 5, RAID 6) due to dedicated processing and caching capabilities, reducing CPU load and improving I/O throughput.
-
Software RAID performance is comparable for simpler RAID levels (RAID 0, RAID 1) and modern CPUs can handle RAID calculations with minimal impact on overall system performance.
-
Write-back caching in hardware RAID (enabled by battery backup units) significantly enhances write speeds, a feature not available in software RAID.
Summary:
-
Choose hardware RAID when high performance, reliability, and advanced RAID features are critical, especially in enterprise or heavy I/O environments.
-
Choose software RAID for cost-sensitive setups, simpler RAID configurations, or when flexibility and ease of integration with the OS are priorities.
This comparison reflects the trade-offs between cost, performance, flexibility, and complexity inherent in hardware vs software RAID implementations.


















Maple Ranking offers the highest quality website traffic services in Canada. We provide a variety of traffic services for our clients, including website traffic, desktop traffic, mobile traffic, Google traffic, search traffic, eCommerce traffic, YouTube traffic, and TikTok traffic. Our website boasts a 100% customer satisfaction rate, so you can confidently purchase large amounts of SEO traffic online. For just 720 PHP per month, you can immediately increase website traffic, improve SEO performance, and boost sales!
Having trouble choosing a traffic package? Contact us, and our staff will assist you.
Free consultation