RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a data storage technology that combines multiple physical hard drives or SSDs into a single logical unit to improve performance, increase storage capacity, and/or provide data redundancy for fault tolerance.
Key Concepts of RAID
-
Data Distribution: RAID stores data across multiple drives using techniques like:
- Disk Striping: Data is split into blocks and distributed across drives to improve speed (e.g., RAID 0).
- Disk Mirroring: Data is duplicated identically on two or more drives for redundancy (e.g., RAID 1).
- Parity: Additional parity data is stored to allow recovery of lost data if a drive fails (e.g., RAID 5, RAID 6).
-
RAID Levels: Different RAID configurations (levels) offer various balances of performance, redundancy, and capacity:
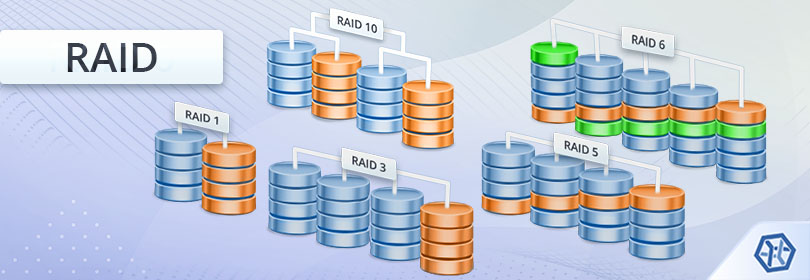
- RAID 0: Striping only, no redundancy, highest performance, but if one drive fails, all data is lost.
- RAID 1: Mirroring, full redundancy, but storage capacity is halved.
- RAID 5: Striping with distributed parity, allows one drive failure without data loss.
- RAID 6: Like RAID 5 but with double parity, tolerates two drive failures.
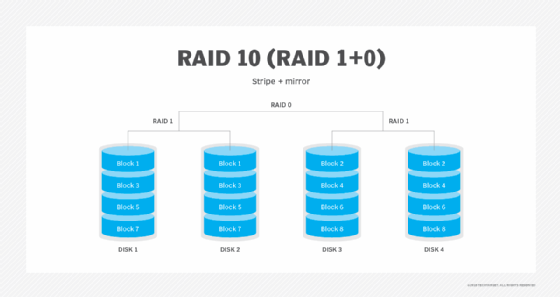
- RAID 10 (1+0): Combines mirroring and striping for both speed and redundancy.
-
Hardware vs Software RAID:
- Hardware RAID uses a dedicated controller to manage the RAID array, offering better performance but higher cost and dependency on the controller.
- Software RAID is managed by the operating system, usually cheaper but may have lower performance.
-
RAID Appearance: To the operating system, a RAID array appears as a single logical drive, simplifying management and use.
Benefits of RAID
- Improved Performance: By spreading data across multiple drives, RAID can increase read/write speeds.
- Fault Tolerance: Certain RAID levels provide redundancy, allowing data to survive one or more drive failures.
- Increased Storage Capacity: RAID can combine the capacity of multiple drives into one large volume.
Considerations
- RAID is not a substitute for backups; it protects against drive failure but not against data corruption, accidental deletion, or disasters.
- Configuration depends on needs: speed, redundancy, capacity, or a combination.
- RAID setup can be complex and requires matching drive configurations to recover data if moved to a new system.
In summary, RAID is a versatile storage technology that balances speed, capacity, and data protection by organizing multiple drives into a single logical unit using various techniques like striping, mirroring, and parity. Different RAID levels serve different needs, and RAID can be implemented via hardware or software depending on performance and cost requirements.

















Maple Ranking offers the highest quality website traffic services in Canada. We provide a variety of traffic services for our clients, including website traffic, desktop traffic, mobile traffic, Google traffic, search traffic, eCommerce traffic, YouTube traffic, and TikTok traffic. Our website boasts a 100% customer satisfaction rate, so you can confidently purchase large amounts of SEO traffic online. For just 720 PHP per month, you can immediately increase website traffic, improve SEO performance, and boost sales!
Having trouble choosing a traffic package? Contact us, and our staff will assist you.
Free consultation