Software-Defined Storage (SDS) is a storage architecture that separates the storage management software from the underlying physical hardware, enabling flexible, scalable, and hardware-agnostic storage solutions. It abstracts storage services from the hardware, allowing diverse storage devices to be pooled and managed as a unified resource without dependence on specific hardware types or vendors.
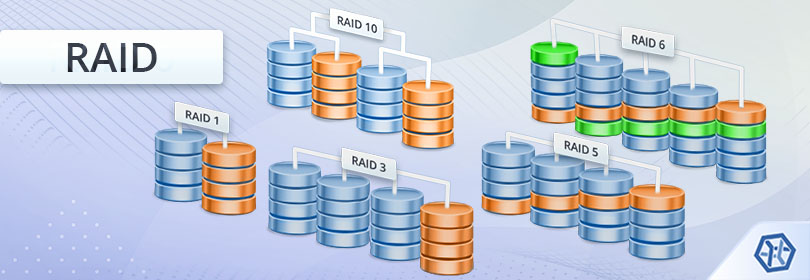
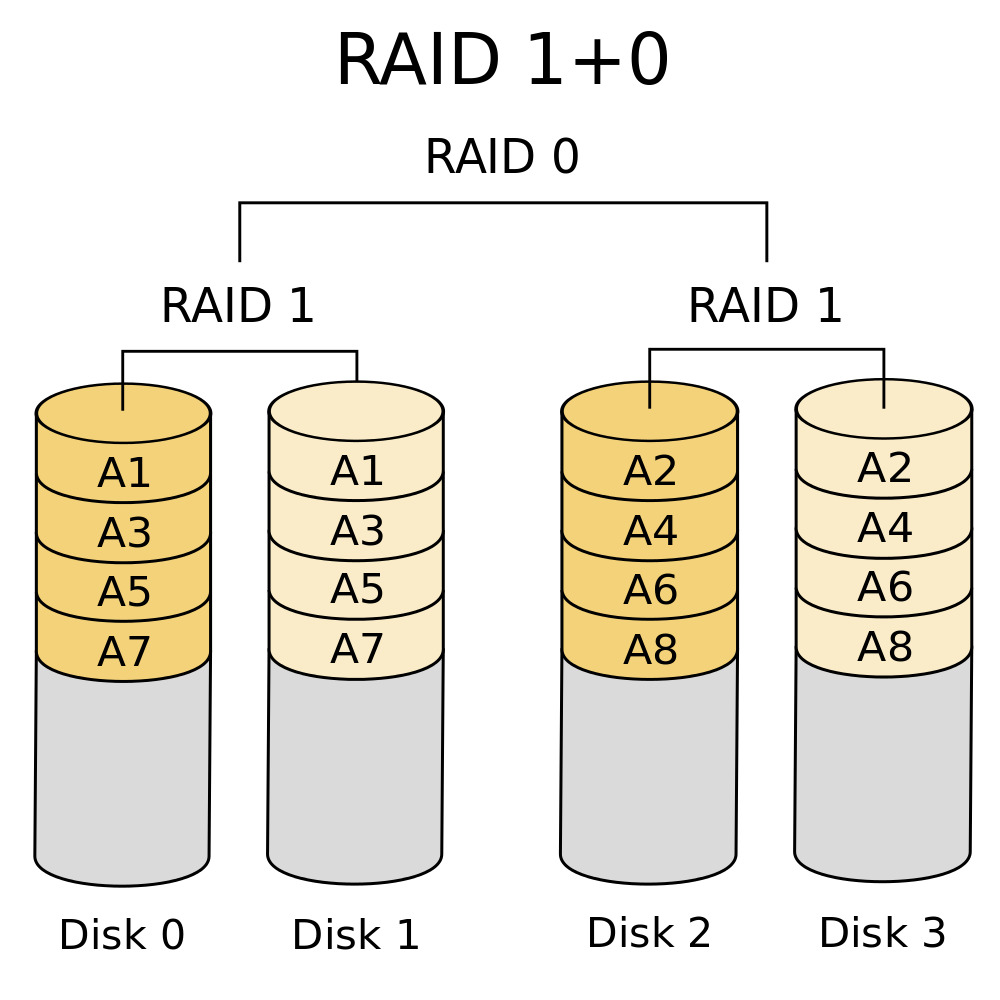
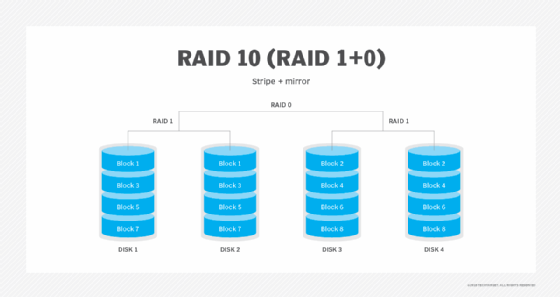
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) technology, on the other hand, is a method of combining multiple physical disks into a single logical unit to provide redundancy, improve performance, or both. RAID can be implemented either in hardware (via dedicated RAID controllers) or in software (managed by the operating system).
Relationship between SDS and RAID
-
RAID as a form of software-defined storage: RAID arrays, especially software RAID, can be considered an early example of software-defined storage because they use software to manage disk redundancy and performance independently of the physical hardware details.
-
SDS extends beyond RAID: While RAID focuses on disk-level redundancy and performance, SDS provides a broader abstraction layer that manages storage volumes, data services, and policies across heterogeneous hardware environments. SDS handles scalability, automation, and quality of service in a distributed manner, often across many nodes, whereas RAID typically operates within a single system or storage array.
-
Software RAID vs. SDS: Software RAID is a component that can be part of an SDS solution, but SDS encompasses much more, including automation, scalability, and heterogeneous hardware support. Software RAID manages disk arrays within an OS, while SDS manages storage resources at a higher level, often across networks and multiple devices.
-
Hardware RAID vs. SDS: Hardware RAID relies on dedicated controllers and is often limited to specific hardware configurations. SDS removes this dependency by abstracting storage services from hardware, enabling more flexible and scalable storage architectures.
Summary Table
| Aspect | RAID (Software/Hardware) | Software-Defined Storage (SDS) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Disk redundancy and performance | Abstracts storage services from hardware |
| Implementation | Software in OS or dedicated hardware controller | Software layer independent of hardware type |
| Hardware Dependency | Hardware RAID requires specific controllers; Software RAID depends on OS compatibility | Hardware-agnostic, supports heterogeneous devices |
| Scalability | Limited to disk arrays or single systems | Scales out across many nodes and devices |
| Management | Manual or OS-based management | Automated, policy-driven, and API-based management |
| Use Case | Data protection and performance within arrays | Flexible, scalable storage infrastructure |
In essence, RAID technology is a foundational data protection and performance technique that can be part of SDS, but SDS represents a more comprehensive, flexible, and scalable approach to managing storage resources across diverse hardware environments.

















Maple Ranking offers the highest quality website traffic services in Canada. We provide a variety of traffic services for our clients, including website traffic, desktop traffic, mobile traffic, Google traffic, search traffic, eCommerce traffic, YouTube traffic, and TikTok traffic. Our website boasts a 100% customer satisfaction rate, so you can confidently purchase large amounts of SEO traffic online. For just 720 PHP per month, you can immediately increase website traffic, improve SEO performance, and boost sales!
Having trouble choosing a traffic package? Contact us, and our staff will assist you.
Free consultation