Here is a comparison of RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6, and RAID 10 focusing on their key differences and typical use cases:
| RAID Level | Minimum Drives | Storage Method | Fault Tolerance | Performance | Storage Efficiency | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAID 1 | 2 | Mirroring (data duplicated on two drives) | Can tolerate 1 drive failure | Good read speed (can read from either drive), write speed similar to single drive | 50% (half of total capacity usable) | Small systems needing simple redundancy, critical data protection with minimal drives |
| RAID 5 | 3 | Block-level striping with distributed parity | Can tolerate 1 drive failure | Good read speed, slower write speed due to parity calculations | (N-1)/N (one drive worth of capacity used for parity) | Read-intensive applications, balanced cost, capacity, and fault tolerance |
| RAID 6 | 4 | Block-level striping with double distributed parity | Can tolerate 2 drive failures | Read speed similar to RAID 5, slower write speed than RAID 5 due to double parity | (N-2)/N (two drives worth of capacity used for parity) | High availability systems needing extra fault tolerance, critical data protection |
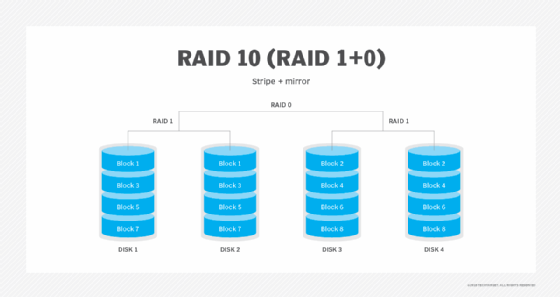
| RAID 10 | 4 | Combination of striping and mirroring (RAID 1+0) | Can tolerate multiple drive failures if not in the same mirrored pair | Excellent read and write performance | 50% (half of total capacity usable) | High-performance databases, transactional systems, environments needing both speed and redundancy |
Key Differences
-
Fault Tolerance:
- RAID 1 and RAID 5 can each tolerate one drive failure.
- RAID 6 can tolerate two simultaneous drive failures, offering better security than RAID 5.
- RAID 10 can tolerate multiple failures as long as no two failures occur in the same mirrored pair.
-
Performance:
- RAID 10 offers the best overall performance for both reads and writes due to striping and mirroring.
- RAID 5 and RAID 6 have good read performance but slower writes because of parity calculations, with RAID 6 being slower than RAID 5.
- RAID 1 improves read speed but write speed is similar to a single drive.
-
Storage Efficiency:
- RAID 1 and RAID 10 use 50% of total raw capacity due to mirroring.
- RAID 5 uses capacity equivalent to total drives minus one for parity.
- RAID 6 uses capacity equivalent to total drives minus two for parity.
-
Minimum Drives Required:
- RAID 1 requires 2 drives.
- RAID 5 requires at least 3 drives.
- RAID 6 requires at least 4 drives.
- RAID 10 requires at least 4 drives.
Use Cases
- RAID 1 is suitable for small setups needing simple redundancy with minimal drives.
- RAID 5 is ideal for read-intensive environments balancing cost, capacity, and fault tolerance.
- RAID 6 is preferred when higher fault tolerance is critical, such as in enterprise storage where two drives might fail simultaneously.
- RAID 10 is best for high-performance applications requiring both speed and fault tolerance, like databases and transactional systems.
This comparison helps in selecting the RAID level that best fits your needs based on performance, fault tolerance, and storage efficiency trade-offs.

















Maple Ranking offers the highest quality website traffic services in Canada. We provide a variety of traffic services for our clients, including website traffic, desktop traffic, mobile traffic, Google traffic, search traffic, eCommerce traffic, YouTube traffic, and TikTok traffic. Our website boasts a 100% customer satisfaction rate, so you can confidently purchase large amounts of SEO traffic online. For just 720 PHP per month, you can immediately increase website traffic, improve SEO performance, and boost sales!
Having trouble choosing a traffic package? Contact us, and our staff will assist you.
Free consultation